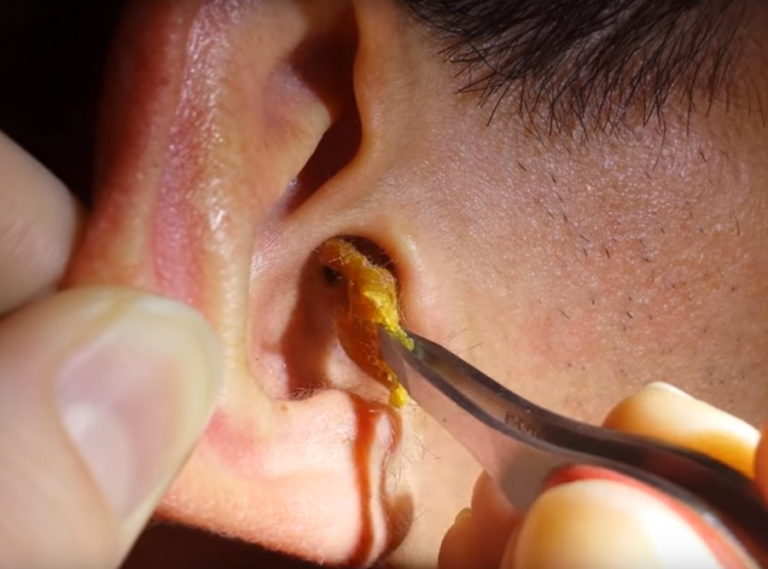
Ear wax removal involves the process of extracting excess cerumen (ear wax) from the ear canal. This is essential to prevent blockages, discomfort, hearing loss, and potential infections. There are several methods for ear wax removal, including home remedies and professional medical procedures.
Ear wax removal is the process of eliminating accumulated cerumen (ear wax) from the ear canal. Ear wax is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear to protect, clean, and lubricate the ear canal. However, excessive ear wax can cause blockages, leading to discomfort, impaired hearing, and potential infections.
During an ear wax removal procedure, the following steps typically occur:
© 2023-2025 Blue Water Urgent Care. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.